Showing posts with label C tutorial. Show all posts
Showing posts with label C tutorial. Show all posts
Sunday, 19 March 2017
8-Bit Binary Addition in C
Binary number system is the system which is used by the computer, it is the key for really fast mathematical computations performed, so let us discuss the logic for 8-bit binary adder step by step.
Prerequisites
- Logic for 8-bit binary to decimal conversion.
- Logic for 8-bit decimal to binary conversion.
- Basic knowledge of bitwise operators.
Above two logic understandings are really important in order to make the inputs and outputs user as well as computer understandable. We'll discuss one full logic in here but it is recommended that you go for step by step explanation by checking out aove mentioned links.
Logic
- Let the user input two operands, as we are dealing with 8-bit format so restrict the input from 0-255.
- Convert the two operands into its binary equivalent and store the results in two separate arrays. Displaying binary equivalent to user is optional but advised.
- Pass the two arrays and the result array as arguments to the function that would do the core computation of adding 8-bit binary numbers.
- Loop bit by bit till 8 bits i.e. from 0 to 7.
- Declaring initial carry bit as 0, do a^b^c and store the result bit in result array, where a is first input array, b is second input array and c is carry
- Evaluate the carry bit by performing ab+bc+ca i.e. (a&b) | (b&c) | (c&a).
- The result array is updated with the final result as the loop terminates.
- Return the carry bit 'c'.
- Check if the carry bit is 1 or 0.
- If it is 1 then print overflow since we are dealing with 8-bit addition and if carry at the end of computation is still 1 then the result would be 9 bits.
- If it is 0 then print the result as binary number and it is recommended to convert the 8 -bit result to its decimal equivalent.
Understanding With Example
- Suppose the input numbers are 11 and 9.
- 8-bit Binary Equivalents: 11-> 00001011 and 9-> 00001001
- c=0,a[0]=1 and b[0]=1, performing result[0]=a^b^c(1^1^0)=0,(X-or returns 0 if two operands are same and 1 if two operands are different,so 1^1=0,1^0=1).
- Carry bit=ab+bc+ca i.e (1&1)+(1&0)+(1&0)=1,(And(&) returns 0 if any of the two bits is 0 and Or(|) returns 1 if any of two bits is 1)
- c=1,a[1]=1,b[1]=0, performing result[1]=a^b^c(1^0^1)=0
- Carry bit=ab+bc+ca i.e (1&0)|(0&1)|(1&1)=1
- c=1,a[2]=0,b[2]=0, performing result[2]=a^b^c(0^0^1)=1
- Carry Bit=ab+bc+ca i.e (0&0)|(0&1)|(1&0)=0
- c=0,a[3]=1,b[3]=1, performing result[3]=a^b^c(1^1^0)=0
- Carry Bit=ab+bc+ca i.e (1&1)|(1&0)|(0&1)=1
- c=1,a[4]=0,b[4]=0,performing a^b^c(0^0^1)=1
- carry Bit=ab+bc+ca i.e (0&0)|(0&1)|(1&0)=0
- Rest all the result bits will be 0.
- Final result array will be 00010100.
- Converting to its decimal equivalent will give 20(11+9).
 |
| 8-Bit binary adder output |
Source Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
void decimal2Binary(int op1, int aOp[]){
int result, i = 0;
do{
result = op1 % 2;
op1 /= 2;
aOp[i] = result;
i++;
}while(op1 > 0);
}
int binary2Decimal(int array[]){
int sum = 0, i;
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++){
if(array[i]) sum += pow(2,i);
}
return sum;
}
void displayBinary(int array[], int n){
int i;
for(i = n -1; i >=0; i--){
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int addBinary(int a1[], int a2[], int result[]){
int i, c = 0;
for(i = 0; i < 8 ; i++){
result[i] = ((a1[i] ^ a2[i]) ^ c); //a xor b xor c
c = ((a1[i] & a2[i]) | (a1[i] &c)) | (a2[i] & c); //ab+bc+ca
}
result[i] = c;
return c;
}
int main(){
int op1, op2, sum;
int a[8] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
int b[8] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
int aSum[8] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
printf("Enter two operands (0 to 255): ");
scanf("%d %d", &op1, &op2);
while(op1 < 0 || op1 > 255 || op2 < 0 || op2 > 255 ){
printf("Enter two operands (0 to 255): ");
scanf("%d %d", &op1, &op2);
}
decimal2Binary(op1, a);
decimal2Binary(op2, b);
printf("Binary Equivalent of %d is ",op1);
displayBinary(a, 8);
printf("Binary Equivalent of %d is ",op2);
displayBinary(b, 8);
if(!addBinary(a, b, aSum)){
printf("Sum of the two number is : ");
displayBinary(aSum, 8);
sum = binary2Decimal(aSum);
printf("Decimal eqivalent is: %d", sum);
}else{
printf("Overflow,crossed 8 bits");
}
return 0;
}
Monday, 13 March 2017
On 21:56 by Vardan Kumar in C tutorial No comments
Binary to Decimal Conversion
Sometimes in a program, the output is in the form of binary number system. Such output is really comfortable for a computing machine to understand but user can not understand such kind of output form i.e. binary output, hence if our program is generating a binary output a functional logic should be written in order to convert that binary to decimal number system.
Logic
- We'll take the input as an array or if we want to take the input directly as an integer then we have to separate the digits of that integer and store the same in an array in reverse order since we are to perform calculations bit by bit. Suppose we enter 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1.
- Next for every 1 in our array we'll add the previous addition with 2 to the power,position of that element in array,
- Since we will store the values in array in reverse order hence 0th index will be 1 followed by 0 at 1st index and so on, giving our array in sequence as 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0.
- Now sum=1*2^0=1 in iteration.(1 at index 0)
- Again for next 1 we will have sum=1+2^2=5.(1 at index 2)
- Again for next 1 we will have sum=5+2^3=13(1 at index 3)
- Since there is no 1 there after hence we have 13 as our binary equivalent for the given input.
 |
| Output Binary to Decimal |
Source Code
#include<Stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int Binary2Decimal(int aBin[]){
int sum = 0, i;
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++){
if(aBin[i])
sum += pow(2,i);
}
return sum;
}
void main()
{
int iBin[8],i,cDec;
printf("Please enter 8 bit binary integer bit by bit\n");
for(i=7;i>=0;i--)
{
scanf("%d",&iBin[i]);
}
cDec=Binary2Decimal(iBin);
printf("The equivalent decimal is %d",cDec);
}
If n bit conversion is required use of macros is recommended in order to write a generic program for the same, logic will be same.
Also Read 8-Bit Decimal to Binary Conversion
On 02:53 by Vardan Kumar in C tutorial No comments
Decimal to Binary Conversion
The most common number system we normally use in ff course decimal number system i.e. numbers from (0-9) but when it comes to computing class decimal number system is not really common rather computer systems use binary number system for computing purposes whether it is digital encoding or a discrete mathematics branch called Boolean Algebra. Hence once should be aware of the logic to convert a decimal number system to its respective binary equivalent.
Logic
We will use the theoretical approach as its programmatic implementation to fulfill our desired purpose of converting decimal number system to its binary twin. Also we'll fetch our result bit by bit so we will use an array to store the bits.
- So first of all we'll take our operand and divide it with two.
- We'll store the remainder as our result bit in the array.
- And we will loop through till our operand is greater than 0.
This was the computation logic. Note in order to display the result we'll traverse the array in reverse order and print the result bit by bit. Also we can modify the number of bits to our desired number, We recommend use of macros for that purpose.
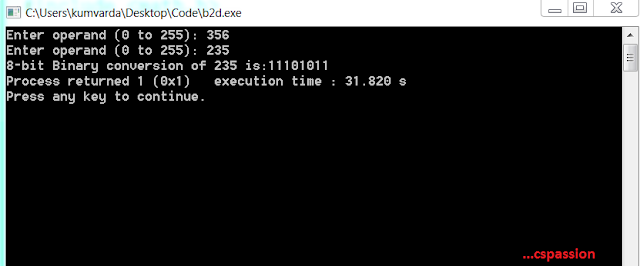 |
| Output:Decimal to Binary Conversion |
Source Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
void Decimal2Binary(int op, int bop[]){
int result, i = 0;
do{
result = op % 2;
op /= 2;
bop[i] = result;
i++;
}while(op > 0);
}
void main()
{
int op,i;
int aOp[8] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
printf("Enter operand (0 to 255): ");
scanf("%d", &op);
while(op < 0 || op > 255)
{
printf("Enter operand (0 to 255): ");
scanf("%d", &op);
}
Decimal2Binary(op, aOp);
printf("8-bit Binary conversion of %d is:",op);
for(i=7;i>=0;i--)
{
printf("%d",aOp[i]);
}
Monday, 27 February 2017
Insertion Sort
It is one of the well known sorting algorithm which is really effective when it comes to sort small number of elements.
Insertion Sort's real life co-relation
- Its implementation is similar to the way one might sort hand of king higher playing cards.
- Initiate with an empty left hand and cards face down on the table.
- Pick one card at once from the table and insert it at its rightful place in the left hand.
- In order to find the correct position of a card, compare it with all the cards already present in the left hand in the right to left direction.
- Note at all times the cards in the left hand are always sorted.
Let us try to understand insertion sort with the help of an example.....
Suppose we have a list of 10 numbers as: 10,32,5,3,98,87,90,45,1,49
- Let us start from 10, Since there is nothing in the left hand so we will directly put 10 in our left hand.
- Next we'll pick 32 from the table, and compare it with 10, since it is larger than 10 so its position will be after 10 in our left hand.
- Now the next number is 5, We'll compare from right to left till we get a number smaller than 5 or we reach the end of the list i.e the left most end, since 5 is smaller than 32 so 32 will be shifted at 5's place,again 5 is smaller than 10 also,hence 10 will be shifted at 32's place,and now we reach the left most end and hence will place 5 over there,so finally there are 5,10,32 on the left hand and 3,98,87,90,45,1,49 on the table.
- Next we'll pick 3, and compare it from right to left direction, after comparing we'll get 3,5,10,32 in the left hand and rest on the table.
- Picking up 98 we don't have any number smaller than this,hence will place 98 at the right most end of left hand making the new list in left hand as 3,5,10,32,98.
- 87 the next number to be inserted before 98 in the left hand making the list as 3,5,10,32,87,98.
- 90 to occupy the position after 87 and before 98, making left hand list as, 3,5,10,32,87,90,98.
- 45 to be picked next from table will be placed after 32 and before 87 to update the list as, 3,5,10,32,45,87,90,98.
- 1 to be placed at the beginning updated the list as 1,3,5,10,32,45,87,90,98.
- Finally the last number on the table to be placed between 45 and 87, making the final sorted list as: 1,3,5,10,32,45,49,87,90,98.
 |
| Insertion Sort Passes |
Source Code:
#include<stdio.h>
# define MAX 20
void main()
{
int soin[MAX],i,j,n,k,swap_var,key;
printf("Enter the number elements needs to be sorted:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\nEnter the list of %d,you want to sort:",n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&soin[i]);
}
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
key=soin[i];
j=i;
while(j>=1&&key<soin[j-1])
{
soin[j]=soin[j-1];
j--;
}
soin[j]=key; // Key inserted at its proper place
printf("\nAfter pass %d list is",i);
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
printf(" %d",soin[k]); //Just for display purpose
}
printf("\nFinal Sorted list is:\n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf(" %d",soin[i]);
Note use of macros is recommended so that code can be made flexible.
Thursday, 23 February 2017
Column alphabets of excel from column numbers in c#
Today we'll discuss method logic to return the column alphabet from the column number as in Microsoft excel in c#. We'll build a generic logic so that it can be implemented in any programming language with change in syntax off course.
For example
If we pass 5 as column number, our method should return E or if we pass 28 our function should return AB.....
So what is the purpose for implementing such a logic? While making an excel sheet programatically, sometimes it is required to implement formulas in a specific cell of excel and respective column alphabetic name is to be listed in the formula expression. So using this logic we can implement formulas dynamically in excel cells.
For example
If we want to apply formula to cells present in column 1 to column 10 as column 1 uses its column members in expression and column 2 uses its members and so on then we'll loop through 1 to 10 and call our function each time incrementing its argument by 1.
 |
| Excel Column Alphabets |
Source Code:
while (count <=55 )
{
cname = get_name(count);
String form = "=" + "SUM(" + cname + "8" + "," + cname + "17" + "," + cname + "53" + "," + cname + "62" + "," + cname + "71" + "," + cname + "80" + "," + cname + "89" + ")";
String form1 = "=" + "SUM(" + cname + "9" + "," + cname + "18" + "," + cname + "54" + "," + cname + "63" + "," + cname + "72" + "," + cname + "81" + "," + cname + "90" + ")";
ExcelApp.Cells[92, count].Formula = form;
ExcelApp.Cells[93, count].Formula = form1;
count++;
}
private String get_name(int c_no)
{
int div = c_no;
string columnName = String.Empty;
int mod;
while (div > 0)
{
mod = (div - 1) % 26;
columnName = Convert.ToChar(65 + mod).ToString() + columnName;
div = (int)((div - mod) / 26);
}
return columnName;
}
The above logic csn be implemented in any programming language just by changing the syntax.
Now let us try to understand the logic:
1. We'll send column no. as 1 to 55 as arguments to our method off course one bt one hence we will make th function call in a loop and catch the return value in a string identifier.
2. Now let us try to understand exhaustively, suppose our method got the argument "28".
3. So c_no(method local variable) got the value 28.
4. div is assigned value of c_no. i.e 28.
5. A string is initialized with name columnName along with an integer variable declared as mod.
6. Now div value is 28 hence we'll loop till it is greater than 0.
- Now inside the loop block we'll assign mod value as (div-1)%26(A-Z) i.e mod will be 1
- Column name will be assigned Ascii value of 65+mod, concatenated with column name retrieved in previous loop traversal i.e column name will be B(ascii value of 66).
- div will be (int)(div-mod)/26 i.e 1 which is greater than zero and hence the loop continues with div as 1.
- Now inside the loop block we'll assign mod value as (div-1)%26(A-Z) i.e mod will be 0
- Column name will be assigned Ascii value of 65+mod, concatenated with column name retrieved in previous loop traversal i.e column name will be A(ascii value of 65)+B(previous column name)=AB.
- div will be (int)(div-mod)/26 i.e 0(Type casting to integer) and since it is not greater than 0,hence the loop exits.
The above logic csn be implemented in any programming language just by changing the syntax.
Monday, 20 February 2017
On 04:16 by Vardan Kumar in C tutorial 1 comment
Addition,Subtraction,Multiplication by 2 and division by 2 without using +,-,* and / in c
When it comes to enhance the software development skills, the magic lies in logic building. So here we are going to discuss a program with can add two numbers,subtract two numbers,multiply by 2 and division by 2,seems simple but here's a twist we can not use +,-,* and / operators for the same.
- Addition:
For the pupose of addition of two numbers off course not by using + operator, we will use ++(increment) as well as --(decrement) operator. Simple! isn't it?. And for the logic we will just decrement one of the number till it gets 0(in a loop) and increment the another one. Let us review the function definition for the same.
int add(int inum1,int inum2)
{
while(inum2--)
{
inum1++;
}
return inum1;
}
2. Subtraction:
Similarly for subtraction we'll use the combination of increment(++) as well as decrement(--) operators since we can not use '-' operator. And for the logic we'll just decrement onre of the number till it gets '0' and decrement the another one. Let us review function definition for the same.
int subtract(int inum1,int inum2)
{
while(inum2--)
{
--inum1;
}
return inum1;
}
int subtract(int inum1,int inum2)
{
while(inum2--)
{
--inum1;
}
return inum1;
}
3. Multiplication By 2:
For the purpose of multiplication by 2 we'll use already built addition function. Got the strike, yeah we will pass the number we want to multiply with '2' as arguments while calling "add" function and store the return value of add function in a pocket variable. Let us review the function definition for the same.
int mulby2(int inum)
{
int pocket;
pocket=add(inum,inum);
return pocket;
}
4. Division By 2:
For the purpose of division by 2 we'll use bitwise operators, yes we got it right, the right shift operator(>>), we'll just right shift the number by '1' we want to divide with 2, hence we'll get the quotient for the division and if we want to get the remainder, off course we know we can use modulus operator(%)
int divby2(int inum)
{
inum = inum>>1;
return inum;
}
Source Code:
#include<stdio.h>
int add(int inum1,int inum2)
{
while(inum2--)
{
inum1++;
}
return inum1;
}
int subtract(int inum1,int inum2)
{
while(inum2--)
{
--inum1;
}
return inum1;
}
int mulby2(int inum)
{
int pocket;
pocket=add(inum,inum);
return pocket;
}
int divby2(int inum)
{
inum = inum>>1;
return inum;
}
void main()
{
int num1,num2,num,ap,as,am,ad;
printf("Enter the two numbers for addition and subtraction:");
scanf("%d %d",&num1,&num2);
printf("\nEnter number for mul and div by 2:");
scanf("%d",&num);
ap=add(num1,num2);
as=subtract(num1,num2);
am=mulby2(num);
ad=divby2(num);
printf("\nResult of addition is:%d",ap);
printf("\nResult of subtraction is:%d",as);
printf("\nResult of multiplication by 2 is:%d",am);
printf("\nquotient of division by 2 is:%d and remainder is %d",ad,num%2);
}
Tuesday, 14 February 2017
On 02:13 by Vardan Kumar in C tutorial No comments
Function which takes string and a character as input and returns the next position of character each time it is called
Today we'll define a function with following properties:-
- Return type of the function will be int i.e. the function will return an integer value.
- Function will accept two arguments.
- One of the argument will be a char and another char array.
Now let us try to understand our purpose with the help of an example......
Suppose our input string is: The domain name of this website is www.cspassion.com
and Suppose our input character is: 'i'
Then our function should do the following...
After 1st call-> 9
After 2nd call->22
After 3rd call->29
After 4th call->33
After 5th call->46
There by if any more calls are made to the function then "No more occurrences" kind of message should be displayed.
Hope the purpose is understood, lets give it a shot before proceeding further......
Logic:
- We'll use infinite while loop which will include switch-case control inside it.
- One case will make a call to function and another will bt he exit case.
- We'll use static variable as function's local variable so that its previous value is not lost whenever a new call is made to the function.
 |
| Output String-Character position Program |
Source code
#include<stdio.h>
int get_position(char linput,char linput1[100])
{
static int count=0;
while(linput1[count]!=linput)
{
count=count+1;
}
count=count+1;
return count;
}
void main()
{
int count=0,pocket,choice,i,count1=0;
char input,input1[100];
printf("Enter the String\n");
fflush(stdin);
fgets(input1,sizeof(input1),stdin);
printf("\nEnter the character whose position you want to return:");
scanf("%c",&input);
for(i=0;i<strlen(input1);i++)
{
if(input1[i]==input)
count1++;
}
while(1)
{
printf("\nEnter 1 to call the function,it would be your call '%d'\n",count+1);
printf("\nEnter 2 for exit\n");
printf("Enter your choice:");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
count=count+1;
if(count<=count1)
{
fflush(stdin);
pocket=get_position(input,input1);
printf("\nAfter call %d,the position is %d\n",count,pocket);
}
else{
printf("No more occurrences of the specified character");
exit(1);
}
break;
case 2:
exit(1);
break;
default:
printf("Invalid input\n");
break;
}
}
}
Tuesday, 7 February 2017
Dynamic financial year date
Many of us come across setting up financial year date dynamically in our code, the reason might be fetching values from your database between one financial year, more precisely the current financial year or we might want to display a header somewhere on your console or application what so ever it may be. The reason or the programming language we intend could be anyone's guess but the logic will be same.
Now everyone would have different start and end date of a financial year, i.e. the date value as well as month value can be hard coded, it would be better if we use macros or const. variable for the same so that if we want to change them at any point of time, we won't need to go through the whole code, we'll just update at the definition of macro or const variable. So what left is yet to be identified and can not be hard coded is the "year".
Let us try to understand it with an example........
Suppose for fiscal year 2017 let us suppose our dates are 01-Jul-2016 to 30-Jun-2017.
So 01-Jul and 30-Jun can be hard coded but we need to identify the current year variation. Lets generalize it. First of all we have to find out today's date
As you generalize the pattern ,if the month value of today's date is less than or equal to '6' then the start date will be 01-Jul-"(Today's date's year value)-1" and the end date will be 30-Jun-"Today's Date's year value" else start date will be 01-Jul-"Today's Date's year" and end date will be 30-Jun-"Today's date year value +1". You might have a clear idea of the logic, if not you ll be having in just couple of minutes by looking at the source code below.
 |
| Dynamic Financial year |
C# Source code for dynamic financial year or fiscal year date
int fy=0;
String start_date, end_date;
DateTime cd = DateTime.Today; //Fetching system's date
int yr = cd.Year; //Parsing year from today's date
if (cd.Month <= 6)
{
start_date = "01-JUL-" + (yr - 1).ToString(); //
end_Date = "30-JUN-" + (yr).ToString();
fy = yr;
}
else
{
start_date = "01-JUL-" + yr.ToString();
end_date = "30-JUN-" + (yr + 1).ToString();
fy = yr + 1;
}
Now since you have the start date and end date strored in the variables we can use them for whatever reason we intend to. Also we can use same logic in any programming language we want just we need to change the syntax. And don't forget to change the fiscal year's date and month value according to your requirement.
Use of macros or const. variables are recommended for the purpose of hard coding the dates.
Thursday, 5 January 2017
On 01:50 by Vardan Kumar in C tutorial No comments
FUNCTIONALITIES IN THE GAME
- Use of File handling to save the game and resuming it from previously save point.
- Random selection of six different combinations of snakes as well as six different ladders every time the game runs.
- A player gets a green signal only if he gets 1 or 6 as dice value.
- A player gets a consecutive turn if he gets 6 as dice value
- Player is demoted to an end point of the snake he hits(off course if hits at a particular position).
Player hit by snake and ladder - A player can only win if he reaches 100 not more or less,for example if he is at 99 and he gets 5,then he is not allowed to move his piece,he can only win if he gets 1).
- A lot more logical constraints are applied so that the logical feasibility of the game is maintained.
SOURCE CODE
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
int ladlower[6]={0,0,0,0,0,0},ladupper[6]={0,0,0,0,0,0},snalow[6]={0,0,0,0,0,0},snaup[6]={0,0,0,0,0,0};
void dissal(int pl,int comp)
{
if(pl<comp)
{
printf("Yipee you got a ladder to %d",comp);
}
else if(pl>comp)
{
printf("oops snake has eaten you to position %d",comp);
}
}
int checkforsal(int player)
{
int i,pos;
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
if (player==ladlower[i])
{
pos=ladupper[i];
break;
}
else if(player==snaup[i])
{
pos=snalow[i];
break;
}
else
{
pos=player;
}
}
return pos;
}
void main()
{
int temp,p1=0,p2=0,di=0,fp1=0,fp2=0,fturn1=1,pocket=0,i;
int j=0;
FILE *f;
char ch,get;
int state=0;
while(1)
{
printf("Press 1 to start new game\n");
printf("Press 2 to resume previous game\n");
fflush(stdin);
srand(time(NULL));
get=getchar();
if(get=='1')
{
state=0;
}
else if(get=='2')
{
state=1;
}
else
{
continue;
}
if(state==1)
{
f=fopen("sal.txt","r");
fread(ladupper,sizeof(ladupper),1,f);
fread(ladlower,sizeof(ladlower),1,f);
fread(snaup,sizeof(snaup),1,f);
fread(snalow,sizeof(snalow),1,f);
fread(&p1,sizeof(int),1,f);
fread(&p2,sizeof(int),1,f);
fread(&fp1,sizeof(int),1,f);
fread(&fp2,sizeof(int),1,f);
fclose(f);
}
else if (state==0)
{
for( i = 0 ; i < 6 ; i++ )
{
j=0;
ladlower[i]=(rand()%90)+1;
ladupper[i]=((ladlower[i]+(rand()%100)+1)%99)+1;
snalow[i]=(rand()%90)+1;
snaup[i]=((snalow[i]+(rand()%100)+1)%99)+1;
if(ladlower[i]>ladupper[i])
{
temp=ladlower[i];
ladlower[i]=ladupper[i];
ladupper[i]=temp;
}
if(snalow[i]>snaup[i])
{
temp=snalow[i];
snalow[i]=snaup[i];
snaup[i]=temp;
}
if(ladupper[i]-ladlower[i]<9&&ladupper[i]<90)
{
ladupper[i]=ladupper[i]+10;
}
if(snaup[i]-snalow[i]<9&&snaup[i]<90)
{
snaup[i]=snaup[i]+7;
}
if(ladupper[i]==snalow[i]||ladupper[i]==snaup[i]
||ladlower[i]==snaup[i]||ladlower[i]==snalow[i])
{
i=i-1;
continue;
}
while(j<i)
{
if(ladupper[j]==snaup[i]||ladlower[j]==snalow[i]||ladlower[j]==snaup[i]||
snalow[j]==snaup[i]||snaup[j]==snaup[i]||snalow[j]==snalow[i]||ladlower[j]==ladlower[i]
||ladupper[j]==ladupper[i])
{
i=i-1;
continue;
}
j++;
}
}
}
printf("\n\t Ladders\t\t Snakes\n");
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
printf("%d\t%02d--->%02d",i+1,ladlower[i],ladupper[i]);
printf("\t\t%02d--->%02d\n",snaup[i],snalow[i]);
}
while(p1!=100&&p2!=100)
{
if(fturn1==1)
{
printf("Player 1 turn:Please press R to roll the dice");
printf("\nPress a to restart the game ");
printf("\nPress s to save and quit the game");
printf("\nPress q to quit without saving");
fflush(stdin);
ch=getchar();
if(ch=='r')
{
di=(rand()%6)+1;
printf("\nWooo!You got %d ",di);
if(p1==0&&(di==1||di==6))
{
fp1=1;
printf("\nYeah you are good to go....");
}
if(fp1==1&&di==6)
{
fturn1=1;
p1=p1+6;
pocket=checkforsal(p1);
dissal(p1,pocket);
p1=pocket;
}
else if(fp1==1&&di!=6)
{
fturn1=0;
p1=p1+di;
pocket=checkforsal(p1);
dissal(p1,pocket);
p1=pocket;
}
else if(fp1==0)
{
printf("\nSorry,you need 1 or 6 to get a green signal");
fturn1=0;
p1=0;
}
if(p1>100)
{
printf("Sorry you cannot cross 100");
p1=p1-di;
}
printf("\nPlayer 1 at position %02d\n",p1);
printf("Player 2 at position %02d\n",p2);
}
else if(ch=='q')
{
exit(0);
}
else if(ch=='a')
{
state=0;
p1=0;
p2=0;
fp1=0;
fp2=0;
fturn1=1;
break;
}
else if(ch=='s')
{
state=1;
f = fopen("sal.txt", "w");
//printf("values are %d %d",snalow[4],snalow[5]);
if(f==NULL)
printf("Unable to open file\n");
fwrite(ladupper, sizeof(ladupper),1 , f);
fwrite(ladlower, sizeof(ladlower), 1 , f);
fwrite(snaup, sizeof(snaup),1 , f);
fwrite(snalow, sizeof(snalow), 1 , f);
fwrite(&p1,sizeof(int),1,f);
fwrite(&p2,sizeof(int),1,f);
fwrite(&fp1,sizeof(int),1,f);
fwrite(&fp2,sizeof(int),1,f);
fclose(f);
exit(0);
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
else
{
printf("Player 2 turn:Please press R to roll the dice");
fflush(stdin);
if(getchar()=='r')
{
di=(rand()%6)+1;
printf("\nWooo!You got %d ",di);
if(p2==0&&(di==1||di==6))
{
fp2=1;
printf("\nYeah you are good to go....");
}
if(fp2==1&&di==6)
{
fturn1=0;
p2=p2+6;
pocket=checkforsal(p2);
dissal(p2,pocket);
p2=pocket;
}
else if(fp2==1&&di!=6)
{
fturn1=1;
p2=p2+di;
pocket=checkforsal(p2);
dissal(p2,pocket);
p2=pocket;
}
else if(fp2==0)
{
printf("\nSorry,you need 1 or 6 to get a green signal");
fturn1=1;
p2=0;
}
if(p2>100)
{
printf("Sorry you cannot cross 100");
p2=p2-di;
}
printf("\nPlayer 1 at position %02d\n",p1);
printf("Player 2 at position %02d\n",p2);
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
}
if(p1==100)
{
printf("\t\t\tPLayer 1 Wins");
}
else if(p2==100)
{
printf("\t\t\tPlayer 2 Wins");
}
else
{
printf("\nThe game has been restarted\n");
}
}
}
Sunday, 19 June 2016
INTRODUCTION
Set bits means the bits that are high i.e. the bits which are set to '1'.
For example:Suppose we enter '10',its binary representation is '1010',so no. of set bits in '10' are '2'.
Here we'll be discussing following two approaches -:
1.Simple Approach
If applying & operation results 0 =>LSB is 0.
If applying & operation results 1 =>LSB is 1.
For example:Let us suppose we enter 10,its binary representation is 1010(Let us take 4 bits for understanding,computer usually represents a number as 32-bit binary in memory).
Let us help you-:
1.Mark the first rightmost set bit.
2.Toggle each bit including the rightmost set bit while moving from right to left direction(from LSB to MSB) until you reach the marked point.
3.The resulting bits are the binary representation of number-1.
FOR EXAMPLE....
For example:Let us suppose we enter 10,its binary representation is 1010(Let us take 4 bits for understanding,computer usually represents a number as 32-bit binary in memory).
1.Applying '&' operation, 1 0 1 0 & 0 0 0 1=0 0 0 0 (Bit wise operation ),since we get 0=>count=0.
2.Right shift number by one,1 0 1 0 >> 1 = 0 1 0 1.
3.Applying '&' operation, 0 1 0 1 & 0 0 0 1 = 0 0 0 1(Bit wise operation),since we get 1=>count=0+1=1.
4.Right shift number by one,0 1 0 1 >> 1 = 0 0 1 0.
5.Applying '&' operation, 0 0 1 0 & 0 0 0 1 = 0 0 0 0(Bit wise operation ),since we get 0=>count=1+0=1.
6. Right shift number by one, 0 0 1 0 >> 1 = 0 0 0 1.
7.Applying '&' operation, 0 0 0 1 & 0 0 0 1 = 0 0 0 1(Bit wise operation ),since we get 1=>count=1+1=2.
8.Right shift number by one, 0 0 0 1 >> 1 = 0 0 0 0.
9.Applying '&' operation, 0 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 1 = 0 0 0 0(Bit wise operation ),since we get 0=>count=2+0=2.
10.Since number is reduced to 0,we'll exit from loop.
2.Brian Kernighans Approach
The idea is to subtract '1' from the number and performing bit wise '&' operation thereby.Now the question is what would subtraction get us,the answer is really simple.Observe the resulting pattern of bits and compare the same with original number.Let us help you-:
1.Mark the first rightmost set bit.
2.Toggle each bit including the rightmost set bit while moving from right to left direction(from LSB to MSB) until you reach the marked point.
3.The resulting bits are the binary representation of number-1.
FOR EXAMPLE....
 |
| Example |
Friday, 25 April 2014
On 23:11 by Vardan Kumar in C tutorial No comments
Let us begin with a brief introduction of C. C is a middle level language that was originally developed by Dennis Ritchie for the Unix operating system. It was first implemented on the Digital Equipment Corporation PDP-11 computer in 1972. It is a middle level language because via C one can develop both system software and application software.
All the application of Unix operating system are virtually written on C language.
All the application of Unix operating system are virtually written on C language.
Main features of C language.
- C follows the Modular programming approach i.e it provides a software design technique to which software is composed of separate parts.
- C programs are Portable i.e they can run on any compiler with a little of no modification.
- C provide wide variety of Data types.
- C provides Bit manipulation i.e we can manage various operation on bit level or we can manage memory on bit level.
- C supports efficient use of pointers.
The only way to learn a new programming language is by writing programs in it.
Let us start with a program...
Print the words
Cspassion - never under estimate the power of passion
It is a hurdle so to leap over it you have to write program text, compile it and run it.
In C the program to print the above text is.
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
printf("Cspassion-never under estimate the power of passion");
}
This running process vary from system to system i.e if you are using UNIX operating system you must create a program in a file whose name ends with extension ".c" ex. cspassion.c, then compile it with command
cc cspassion.c
if you haven't botched anything, such as omitting a character or misspelling something, the compilation will complete silently and it makes a executable file named, cspassion.out
if you run a.out by typing the command
cspassion.out
it will print
Cspassion-never underestimate the power of passion!
The output screen will be like this
A C program always consists of functions and variables. A function contains statements that specifies the computing operation to be done and variables stores values stored during computation.
Explanation of above program
- #include<stdio.h>:- This line tells the compiler to include the information about standard input/output libraries. This line always appear at the beginning of C source file.
- main():-This defines a function named main that receives no argument values. program always begins executing at the beginning of main. Main usually call other functions to help perform its job, some that you wrote.
- { }:- These are braces. statements of main function are enclosed in braces.
- printf("cspassion- never under estimate the power of passion!"); :-As the function is always called by naming it, followed by parenthesized list of arguments. here printf is a function with s a list of arguments in the form of character strings.
Note:-
- printf never supplies a new line automatically.
- \n is used in C notation for newline character.
- among other C also provides \t for tab, \b for backspace, \" for double quote, \\ for backslash itself.
Viva Questions???
- Who developed the C language And in which year? (Dennis Ritchie in 1972 ).
- Why C is a middle level language? (because via C one can make both system software and application software?
Let me ask you some questions?
- As main function calls other function and we also know that main is also a function then tell me main is called by_____?
- printf("cspassion
");
Will the compiler accept this format?
By:Hardik Thakral
By:Hardik Thakral
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Search
Popular Posts
-
Troubleshooting Cisco VPN client Before starting troubleshooting, Let us see what VPN is and what it requires to perform its intended f...
-
File Versioning C# File versioning, saving file with unique file name in c# File versioning allows a user to have several versions of ...
-
Evolution-Mobile Phones With the development of portable technology,wireless communication has so evolved that (According to the announce...
-
Text Box Hint in c# Windows Form Application Text Box Hint in c# Windows Form Application While developing a windows form applicat...
-
Unable to set the Freeze Panes property of Window Class C# It is generally easy to resolve the compile time errors because the reason fo...











