Showing posts with label C#. Show all posts
Showing posts with label C#. Show all posts
Thursday, 30 March 2017
On 00:20 by Vardan Kumar in C# No comments
How to get all the file names which contains a particular word
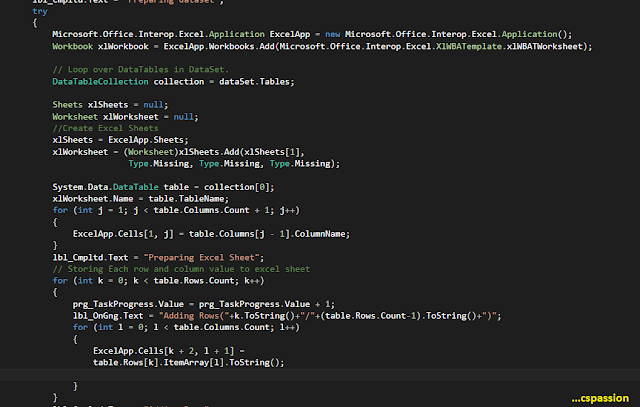
Analysis is the most important step which every software development life cycle requires to avoid rework. Sometimes it becomes a tedious task and could eat up a lot of time hence increasing cost of software development. For example: Some code changes in the current system needs to be implemented, changes like you have to change a particular identifier name to another in the entire system. So if this process is needed to be carried out professionally then the impact analysis of that identifier should be captured. So what would you open each and every source file, header files or what ever your system contains and try to capture, how many times the identifier hits in a particular file, well reading thousands of files having thousands of line definitely not feasible. So instead of manually doing this task, automation should be implemented for the same.
So let us make c# windows form application which will take directory as well as identifier name from the user and returns a txt file or excel file or what ever format you want and get all the file names along with the number of hits of a word in a particular file.
Prerequisites
Logic
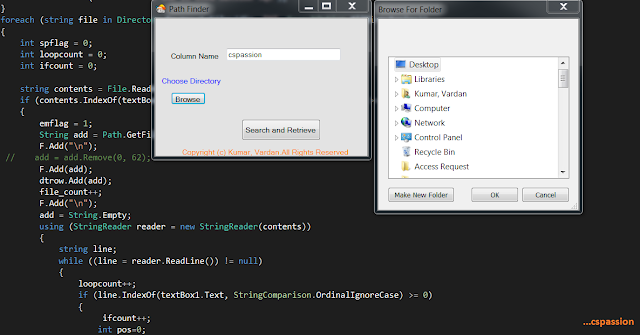
- Let the user enter the identifier name and select the directory.
- Validations should be applied i.e if user leaves the field blank or do not select a directory.
- if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(textBox1.Text)){MessageBox.Show("Please enter identifier name");return;}
- We'll use a list<string> to add as one complete row to data table which in turn will become one row of excel.
- The contents of <list string> will be in sequence, first the name of file and second the no. of hits corresponding to that file.
- The list will be added as row to data table.
- List will be cleared so as to populate a row for next file in data table.
- Add columns to data table giving your desired names. Also check if data table already contains columns, what if a user in a single run search and retrieve more than once.
- if(dt.Columns.Count==0)
{dt.Columns.Add("Programs referencing SAK");dt.Columns.Add("Total No. of Hits for SAK");
} - Now for each file in the selected directory enabling search option to search all directories and specifying desired file format(* to search all file formats).
- foreach (string file in Directory.EnumerateFiles(dir, "*", SearchOption.AllDirectories).
- Copy all the contents of the file at once in a string.
- string contents = File.ReadAllText(file);
- Check if the entered identifier name exist in that file.
- if (contents.IndexOf(textBox1.Text, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) >= 0
- Use string extension to ignore case.
- public static class StringExtensions{public static bool Contains(this string source, string toCheck, StringComparison comp){return source.IndexOf(toCheck, comp) >= 0;}}
- If the file contains the identifier name then add the file name to list string.
- String add = Path.GetFileName(file);dtrow.Add(add);add = String.Empty; //To clear string for next file.
- Now since we are sure that the current file contains at least an occurrence of entered identifier name we will read the contents copied to the string line by line.
- using (StringReader reader = new StringReader(contents)){string line;while ((line = reader.ReadLine()) != null)
- Now check if identifier exists in the current line, again ignoring case
- if (line.IndexOf(textBox1.Text, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) >= 0)
- Now if identifier exists in that line, count the total number of occurrences of the identifier in that line.
- while ((pos < line.Length) && (pos = line.IndexOf(textBox1.Text,pos,StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) != -1){ofile_occur++;pos += textBox1.Text.Length;}
ofile_occur = 0; // for re-use - pfilr_occur=pfilr_occur+ofile_occur;
- Now after reading all the lines of a particular file. pfilr_occur contains all the hits of that particular file. Just add that to list<string> and that list string as a row to data table. Don't forget to clear the list string to re-use and the file occurrence variable
- dtrow.Add(pfilr_occur.ToString());dt.Rows.Add(dtrow.ToArray<string>());dtrow.Clear();pfilr_occur = 0;.
- Repeat the above steps for each and every file.
- Finally after traversing through all the files in all the directories as well as sub-directories as specified by the user data table dt is ready.
- Now just populate the excel sheet using that data table.
- Click here to know How to populate excel file from dataset or datatable in c#.
- Excel sheet is ready make it visible to use and save the excel sheet, if you want to specify a unique path for the excel file for the sake of file versioning
- click here to read How to use file versioning, saving file with unique file path in c#.
- Note: Folder Browser dialog is used for user to select a directory.
- private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){DialogResult result = folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog();if (result == DialogResult.OK){dir = folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;label3.Text = dir;tt.SetToolTip(label3, label3.Text); // How to set tool tip in c#}}
- Also if the identifier name is not found then a message box should be displayed.
- else{MessageBox.Show("Column name not found in any of the files in specified directory");}
 |
| File name along with number of hits in c# |
Source Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication3
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
System.Data.DataSet dataSet = null;
System.Data.DataTable dt = new System.Data.DataTable("sak_impact");
int file_count = 0;
int occur_count=0;
int total = 0;
int ofile_occur = 0;
int pfilr_occur = 0;
List<String> dtrow=new List<String>();
ToolTip tt = new ToolTip();
String dir = String.Empty;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int emflag = 0;
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(textBox1.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("Please enter identifier name");
return;
}
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(dir))
{
MessageBox.Show("Please Choose a directory");
return;
}
if(dt.Columns.Count==0)
{
{
dt.Columns.Add("Programs referencing SAK");
dt.Columns.Add("Total No. of Hits for SAK");
}
}
foreach (string file in Directory.EnumerateFiles(dir, "*", SearchOption.AllDirectories))
{
string contents = File.ReadAllText(file);
if (contents.IndexOf(textBox1.Text, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) >= 0)
{
emflag = 1;
String add = Path.GetFileName(file);
dtrow.Add(add);
add = String.Empty;
using (StringReader reader = new StringReader(contents))
{
string line;
while ((line = reader.ReadLine()) != null)
{
if (line.IndexOf(textBox1.Text, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) >= 0)
{
int pos=0;
while ((pos < line.Length) && (pos = line.IndexOf(textBox1.Text,pos,StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) != -1)
{
ofile_occur++;
pos += textBox1.Text.Length;
}
pfilr_occur=pfilr_occur+ofile_occur;
ofile_occur = 0;
}
}
}
dtrow.Add(pfilr_occur.ToString());
dt.Rows.Add(dtrow.ToArray<string>());
dtrow.Clear();
pfilr_occur = 0;
}
}
if (emflag == 1)
{
dataSet = new DataSet("General");
dataSet.Tables.Add(dt);
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application ExcelApp = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
Workbook xlWorkbook = ExcelApp.Workbooks.Add(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlWBATemplate.xlWBATWorksheet);
// Loop over DataTables in DataSet.
DataTableCollection collection = dataSet.Tables;
Sheets xlSheets = null;
Worksheet xlWorksheet = null;
//Create Excel Sheets
xlSheets = ExcelApp.Sheets;
xlWorksheet = (Worksheet)xlSheets.Add(xlSheets[1],
Type.Missing, Type.Missing, Type.Missing);
System.Data.DataTable table = collection[0];
xlWorksheet.Name = table.TableName;
for (int j = 1; j < table.Columns.Count + 1; j++)
{
ExcelApp.Cells[1, j] = table.Columns[j - 1].ColumnName;
}
// Storing Each row and column value to excel sheet
for (int k = 0; k < table.Rows.Count; k++)
{
for (int l = 0; l < table.Columns.Count; l++)
{
ExcelApp.Cells[k + 2, l + 1] =
table.Rows[k].ItemArray[l].ToString();
}
}
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.WindowState = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlWindowState.xlMaximized;
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.FreezePanes = false;
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.SplitColumn = 1;
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.SplitRow = 1;
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.FreezePanes = true;
ExcelApp.Columns.AutoFit();
// xlWorkbook.SaveAs("");
ExcelApp.Visible = true;
((Worksheet)ExcelApp.ActiveWorkbook.Sheets[ExcelApp.ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Count]).Delete();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Column name not found in any of the files in specified directory");
}
}
private void label2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DialogResult result = folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog();
if (result == DialogResult.OK)
{
dir = folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
label3.Text = dir;
tt.SetToolTip(label3, label3.Text);
}
}
}
public static class StringExtensions
{
public static bool Contains(this string source, string toCheck, StringComparison comp)
{
return source.IndexOf(toCheck, comp) >= 0;
}
}
}
Wednesday, 22 March 2017
Unable to set the Freeze Panes property of Window Class C#
It is generally easy to resolve the compile time errors because the reason for the error is probably known but a run time error always hinders the development process for a considerable amount of time so are the exceptions that unknowingly show up from no where. That is why it is always advised to handle each and every exception your application might throw. The only way to be a master in handling exception is experience, yeah you read it right. More you develop, more problem you will encounter in your developing environment and in turn more you will know the reason and the so called timing of the exceptions.
Exception
One of the most encountered is "unable to set freeze panes property of window class" which show up when you try to freeze panes while formatting an excel file in c#.
Reason
The main reason for occurrence of such an exception is incompatibility between older and the newer versions of MS Excel.
When it occirs
This exception occurs when you are using a newer version of MS Excel and your application gets activate in background, I repeat your MS Excel application thread opens in the minimized state which hinders the freezing pane process.
How to counter this exception?
Obviously to get a solution to a problem, first of all understanding the problem is must more precisely the reason of problem should be known. Since we know the reason why freeze panes property is not set and the exception is thrown we can provide a solution.
So if somehow we can make our MS Excel thread open in maximized state or normal state explicitly then bingo we successfully resolved the issue.
Still it is a good practice to surround the exception causing snippet with try block and catch the exception so that there is no exceptional flow change in your application.
Let us look at the source code for the same
Exception
One of the most encountered is "unable to set freeze panes property of window class" which show up when you try to freeze panes while formatting an excel file in c#.
Reason
The main reason for occurrence of such an exception is incompatibility between older and the newer versions of MS Excel.
When it occirs
This exception occurs when you are using a newer version of MS Excel and your application gets activate in background, I repeat your MS Excel application thread opens in the minimized state which hinders the freezing pane process.
How to counter this exception?
Obviously to get a solution to a problem, first of all understanding the problem is must more precisely the reason of problem should be known. Since we know the reason why freeze panes property is not set and the exception is thrown we can provide a solution.
So if somehow we can make our MS Excel thread open in maximized state or normal state explicitly then bingo we successfully resolved the issue.
Still it is a good practice to surround the exception causing snippet with try block and catch the exception so that there is no exceptional flow change in your application.
 |
| Unable to Set Freeze Panes Exception |
Let us look at the source code for the same
Source Code
//Maximize the window state before setting freeze panes property
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.WindowState = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlWindowState.xlMinimized;
ExcelApp.Columns.AutoFit();
try
{
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.FreezePanes = false;
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.SplitColumn = 1; //To freeze first column
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.SplitRow = 1; // To freeze Top Row
ExcelApp.Application.ActiveWindow.FreezePanes = true;
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
}
Also Read Troubleshooting Cisco VPN client 0x8004a029 with screenshots
Also Read Troubleshooting ORA-12505
Also Read Troubleshooting ORA-12505
Monday, 20 March 2017
On 21:22 by Vardan Kumar in C# 8 comments
File versioning, saving file with unique file name in c#
File versioning allows a user to have several versions of a file simultaneously at a particular path. Not only it intimates a user of which is the latest version i.e generated at a later stage or an older version but also provides a unique file name in the same directory.
For example....
Suppose a report generation application is developed which saves a user-readable file as an output, as discussed in earlier posts also an efficient GUI(Graphical user interface) is the most interactive one i.e. a GUI in which a user feels to have control over the application. In such an application a user is generally provided with the privilege to select his/her desired path. It is a general tendency of a computer operating individual to select same path as well as name each time he/she wants to generate the report. Now suppose user chooses a file name as cspassion.xlsx and the same file name already exists at that path, so an efficient application would save the latest version of report as cspassion(1).xlsx or cspassion(2).xlsx to avoid exception or prompting user to select if he/she wants to replace the previous version of file or not, also this would take the control from your application to the operating system which should generally be avoided as much as possible.
Logic
- First of all user selected file name or path is sent as an argument to the method fetching unique file path or creating file versions.
- Now we will check if the file already exists at that directory or not
- If not then return that file path and save the file with user selected file name at his/her desired path.
- If yes then continue with the version generation.
- Now split and store directory,file name as well as extension in different identifiers.
- Initialize number as 1,if you want to display (2) as file version after first version and initialize to 0 if you want it as (1) after first version.
- Now we'll check if a version after initial version is generated using regular expression match
- If it matches then we'll extract file name from group 1 and number from group 2.
- Now we have number as well as file name we'll loop through while the file exists in that path.
- We'll increment number by 1 in each iteration
- Format the string as filename,(number) and extension.
- Return the file path and save the workbook.
I have generated five versions of same file named cspassion for reference in current directory. Refer to image below
 |
| File Versioning C# |
Source Code
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
using Oracle.DataAccess.Client;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Xml;
using System.IO;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication2
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
string s_oRcConnectionString = null; //Click here to know how to set dynamic connection string c#
ToolTip tt = new ToolTip();
string uniquepath=String.Empty;
private void btn_Save(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
xlWorkbook.SaveAs(uniquepath);
}
private void btn_Browse_Click_1(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog1 = new SaveFileDialog();// using save file dialog
saveFileDialog1.Filter = "Excel|*.xlsx";
saveFileDialog1.Title = "Save Excel report";
if (saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
lbl_Path.Text = saveFileDialog1.FileName;
tt.SetToolTip(lbl_Path, lbl_Path.Text); // click here to read how to set tool tip for controls
lbl_Path.Visible = true;
string path=lbl_Path.Text;
uniquepath=GetUniqueFilePath(path);
}
public static string GetUniqueFilePath(string filepath)
{
if (File.Exists(filepath))
{
string fold = Path.GetDirectoryName(filepath);
string filename = Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(filepath);
string extension = Path.GetExtension(filepath);
int number = 1;
Match regex = Regex.Match(filepath, @"(.+) \((\d+)\)\.\w+");
if (regex.Success)
{
filename = regex.Groups[1].Value;
number = int.Parse(regex.Groups[2].Value);
}
do
{
number++;
filepath = Path.Combine(folder, string.Format("{0} ({1}){2}", filename, number, extension));
}
while (File.Exists(filepath));
}
return filepath;
}
}
}
Thursday, 2 March 2017
How to give save path through browse button c#
For an application to be user friendly, it is necessary to provide maximum accessibility features. Since our application should follow abstraction and should focus on hiding complexities to user, so a good GUI(Graphical user interface) with accessibility features will show your hard work while building the application. No matter how much you burn midnight oil while developing back-end of your application, if it lacks a good GUI with accessibility features it is definitely in vain.
If your application generates a file, which user is supposed to read or gather information then giving privilege of choosing the save path for the file to user is always nice. Button control is the best way to do this.
Logic
- Firstly we'll create a button click event.
private void btn_Browse_Click_1(object sender, EventArgs e)
2. Now we'll create an instance of SaveFileDIalog.
SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog1 = new SaveFileDialog();
3.Now we'll set the filter for our save file dialog that is what kind of file user should be prompted to save which is shown under save as type drop down. Multiple filters are separated by vertical bar.
saveFileDialog1.Filter = "Excel|*.xlsx";
4.Now we'll give title to our dialog box.
saveFileDialog1.Title = "Save Excel report";
5.Now we'll call ShowDialog method and if method return value seems correct then we'll assign the path to our desired label, off course we want to store the file path selected by user to use it further. If you don't want to display the path selected by user you can also use a string identifier to store the path.
if (saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
lbl_Path.Text = saveFileDialog1.FileName;
Note: Don't forget to change other characteristics of label if any after changing its text such as tool tip etc.
 |
| Path Before clicking browse button |
 |
| Save File Dialog Box |
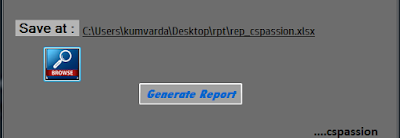 |
| Save Path after selecting path |
Source Code
private void btn_Browse_Click_1(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Instance creation
SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog_csp = new SaveFileDialog();
// Seting filter
saveFileDialog_csp.Filter = "Excel|*.xlsx";
// Giving title
saveFileDialog_csp.Title = "Save Excel report";
// show dialog box
if (saveFileDialog_csp.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
// Storing the path
lbl_Path.Text = saveFileDialog_csp.FileName;
// Changing tool tip
tt.SetToolTip(lbl_Path, lbl_Path.Text);
// Making label visible
lbl_Path.Visible = true;
}
Thursday, 23 February 2017
Column alphabets of excel from column numbers in c#
Today we'll discuss method logic to return the column alphabet from the column number as in Microsoft excel in c#. We'll build a generic logic so that it can be implemented in any programming language with change in syntax off course.
For example
If we pass 5 as column number, our method should return E or if we pass 28 our function should return AB.....
So what is the purpose for implementing such a logic? While making an excel sheet programatically, sometimes it is required to implement formulas in a specific cell of excel and respective column alphabetic name is to be listed in the formula expression. So using this logic we can implement formulas dynamically in excel cells.
For example
If we want to apply formula to cells present in column 1 to column 10 as column 1 uses its column members in expression and column 2 uses its members and so on then we'll loop through 1 to 10 and call our function each time incrementing its argument by 1.
 |
| Excel Column Alphabets |
Source Code:
while (count <=55 )
{
cname = get_name(count);
String form = "=" + "SUM(" + cname + "8" + "," + cname + "17" + "," + cname + "53" + "," + cname + "62" + "," + cname + "71" + "," + cname + "80" + "," + cname + "89" + ")";
String form1 = "=" + "SUM(" + cname + "9" + "," + cname + "18" + "," + cname + "54" + "," + cname + "63" + "," + cname + "72" + "," + cname + "81" + "," + cname + "90" + ")";
ExcelApp.Cells[92, count].Formula = form;
ExcelApp.Cells[93, count].Formula = form1;
count++;
}
private String get_name(int c_no)
{
int div = c_no;
string columnName = String.Empty;
int mod;
while (div > 0)
{
mod = (div - 1) % 26;
columnName = Convert.ToChar(65 + mod).ToString() + columnName;
div = (int)((div - mod) / 26);
}
return columnName;
}
The above logic csn be implemented in any programming language just by changing the syntax.
Now let us try to understand the logic:
1. We'll send column no. as 1 to 55 as arguments to our method off course one bt one hence we will make th function call in a loop and catch the return value in a string identifier.
2. Now let us try to understand exhaustively, suppose our method got the argument "28".
3. So c_no(method local variable) got the value 28.
4. div is assigned value of c_no. i.e 28.
5. A string is initialized with name columnName along with an integer variable declared as mod.
6. Now div value is 28 hence we'll loop till it is greater than 0.
- Now inside the loop block we'll assign mod value as (div-1)%26(A-Z) i.e mod will be 1
- Column name will be assigned Ascii value of 65+mod, concatenated with column name retrieved in previous loop traversal i.e column name will be B(ascii value of 66).
- div will be (int)(div-mod)/26 i.e 1 which is greater than zero and hence the loop continues with div as 1.
- Now inside the loop block we'll assign mod value as (div-1)%26(A-Z) i.e mod will be 0
- Column name will be assigned Ascii value of 65+mod, concatenated with column name retrieved in previous loop traversal i.e column name will be A(ascii value of 65)+B(previous column name)=AB.
- div will be (int)(div-mod)/26 i.e 0(Type casting to integer) and since it is not greater than 0,hence the loop exits.
The above logic csn be implemented in any programming language just by changing the syntax.
Wednesday, 22 February 2017
On 00:17 by Vardan Kumar in C# No comments
Excel sheet from data table and data set in c#
Excel workbook is one of the most popular MS office application, especially when it comes to make a report. Hence it is recommended to learn how to make an excel sheet in c# developing environment.
Before we continue let us briefly understand what a DataSet is:
A DataSet is a collection of data tables objects or instances on which we can set relation through data relation objects and hence navigate through data table architecture.
How DataSet is declared or initialized in c#?
System.Data.DataSet dt_csp = null;
Next we'll declare our data table:
System.Data.DataTable tb_csp = new System.Data.DataTable("SFY" + sfy.ToString());
Here the DataTable method argument is its name which will also be used as the name of our excel sheet which we are just about to make.
sfy is an integer variable which can be set dynamically as financial year value.
We can populate our data table using:
tb_csp.Columns.Add("cspassion Column String"); // To add columns to data table
Note for data table the columns name should be unique otherwise it will throw an exception
tb_csp.Rows.Add("cspassion Row String"); // To add rows to data table
After populating the data table, add it to data set.
dt_csp = new DataSet("General");
dt_csp.Tables.Add(tb_csp);
Hence our data table is added to data set colection.
So we are ready with our data set, now let us populate our excel sheet
- Firstly we have to make an object of Microsoft office excel application Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application ExcelCsp = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
- Now we'll create a workbook. Workbook xlWorkbook = ExcelCsp.Workbooks.Add(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlWBATemplate.xlWBATWorksheet);
- Now we'll create a data table collection and add our data set tables to it. DataTableCollection collection = dataSet.Tables;
- Now we'll initialize Sheets and worksheets and create our excel sheets.
Sheets xlSheets = null
Worksheet xlWorksheet = null;
//Create Excel Sheets
xlSheets = ExcelCsp.Sheets;
xlWorksheet = (Worksheet)xlSheets.Add(xlSheets[1], Type.Missing, Type.Missing, Type.Missing);
7.Now we'll add our collection first table to a data table and give our worksheet the same name as data table.
System.Data.DataTable table_csp = collection[0];
xlWorksheet.Name = table_csp.TableName;
8.Now we'll add columns to our excel sheet.
for (int j = 1; j < table_csp.Columns.Count + 1; j++)
{
ExcelCsp.Cells[1, j] = table.Columns[j - 1].ColumnName;
}
9. Now we'll store value of each row and column to excel sheet.
for (int k = 0; k < table_csp.Rows.Count; k++)
{
for (int l = 0; l < table_csp.Columns.Count; l++)
{
ExcelCsp.Cells[k + 2, l + 1] =
table_csp.Rows[k].ItemArray[l].ToString();
}
Source Code:
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application ExcelCsp = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
Workbook xlWorkbook = ExcelApp.Workbooks.Add(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlWBATemplate.xlWBATWorksheet);
DataTableCollection collection = dataSet.Tables;
Sheets xlSheets = null;
Worksheet xlWorksheet = null;
//Create Excel Sheets
xlSheets = ExcelCsp.Sheets;
xlWorksheet = (Worksheet)xlSheets.Add(xlSheets[1],
Type.Missing, Type.Missing, Type.Missing);
System.Data.DataTable table_csp = collection[0];
xlWorksheet.Name = table_csp.TableName;
for (int j = 1; j < table_csp.Columns.Count + 1; j++)
{
ExcelCsp.Cells[1, j] = table_csp.Columns[j - 1].ColumnName;
}
for (int k = 0; k < table_csp.Rows.Count; k++)
{
for (int l = 0; l < table_csp.Columns.Count; l++)
{
ExcelCsp.Cells[k + 2, l + 1] =
table_csp.Rows[k].ItemArray[l].ToString();
}
}
//We have populated our excel sheet successfully, but what now we have to save it also....
xlWorkbook.SaveAs("path");
// And finally make our excel sheet visible
ExcelCsp.Visible = true;((Worksheet)ExcelCsp.ActiveWorkbook.Sheets[ExcelCsp.ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Count]).Delete();
Tuesday, 14 February 2017
Progress Bar in C# Windows form application
Why Progress Bar is important?
Lets imagine ourselves as a user of an application. Now lets suppose our application is taking a minute or two to do its desired purpose. Meantime application is doing nothing, we are just seeing a dumb windows form in front of you, what would we think...Well yes we would think that the application hung up in about 20 to 30 sec or less and would try to interrupt the application progress either by closing it or opening task manager and what not?
Hence it is considered a good practice as a developer to tell our user the progress of our application. Hope we have understood the main purpose of a progress bar, apart from it makes our GUI look better.
Including a progress bar is not just enough, incorporating an efficient progress bar which should move continuously is also necessary as suppose if progress bar has stopped progressing for about 20-30 sec, again we as a user would think that application has stopped responding.
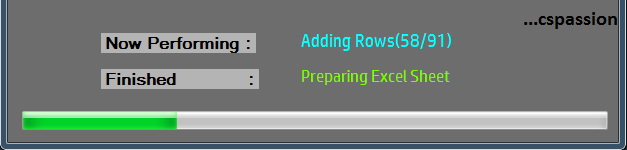
Also additionally,
- if we can tell the user what application is currently doing that would be nice.
- We will also try to increase the progress of the progress bar linearly or monotonously as far as possible which we can do by increasing its progress in a loop.
 |
| Progress Bar c# |
try
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application ExcelApp = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
Workbook xlWorkbook = ExcelApp.Workbooks.Add(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlWBATemplate.xlWBATWorksheet);
DataTableCollection collection = dataSet.Tables;
Sheets xlSheets = null;
Worksheet xlWorksheet = null;
//Create Excel Sheets
xlSheets = ExcelApp.Sheets;
xlWorksheet = (Worksheet)xlSheets.Add(xlSheets[1],
Type.Missing, Type.Missing, Type.Missing);
System.Data.DataTable table = collection[0];
xlWorksheet.Name = table.TableName;
for (int j = 1; j < table.Columns.Count + 1; j++)
{
ExcelApp.Cells[1, j] = table.Columns[j - 1].ColumnName;
}
lbl_Cmpltd.Text = "Preparing Excel Sheet";
// Storing Each row and column value to excel sheet
for (int k = 0; k < table.Rows.Count; k++)
{
prg_TaskProgress.Value = prg_TaskProgress.Value + 1;
lbl_OnGng.Text = "Adding Rows("+k.ToString()+"/"+(table.Rows.Count-1).ToString()+")";
for (int l = 0; l < table.Columns.Count; l++)
{
ExcelApp.Cells[k + 2, l + 1] =
table.Rows[k].ItemArray[l].ToString();
}
}
lbl_Cmpltd.Text = "Adding Rows";
Features and Logic
- Above Source code populates an excel sheet via data tables in data set
- In above code table.rows.Count gives the total number of rows and hence our loop runs the same number of times
- k will take values from 0 to total number of rows in data table
- Progress Bar's value is incremented by '1' each time the loop is executed.
- Progress Bar's maximum value should be set in its properties and its value should not exceed that maximum value or else it will throw an exception.
- We can also change the style of our progress bar,I prefer continuous style for elegant looks.
- Providing labels for what currently our application is performing makes our application more sophisticated.
Sunday, 12 February 2017
Reading multiple columns from database
Most of the application development isn't possible without using a Database Management System since our aim is never to build a normal application, our aim is to build a sophisticated application. So database applications must be included within our developing environment. While fetching information or values from our database we might come across retrieving values from multiple columns, usually can be done if we have same query structure for data retrieval i.e. conditions applied on data are similar. Here we'll be using oracle DBMS but you can use any for the same. Hence instead of using multiple queries to retrieve data from multiple columns, we'll use a single query to read multiple columns.
In order to fetch data from database we'll use Oracle data reader and loop the data table until the last record. Before proceeding to source code we must know how reader works?
Reader is basically used to retrieve row values. For explanation purpose let us imagine the data table as a matrix[i x j].
reader[0] will read the value at [1,1]
reader[1] will read value at [1,2]
.
.
.
.
.
reader[j] will read value at [1,j]
When the full row is read then the reader will jump to the next row and read till the full row is fetched.
 |
| Reading Multiple Columns from database c# source code |
Now assuming that we all have basic knowledge for database, function of oracle data reader and basics to retrieve values from database in c#, we'll jump to the source code.
// Variable Declaration
List<string> AN = new List<string>();
List<string> BN = new List<string>();
List<string> CN = new List<string>();
List<string> DN = new List<string>();
List<string> EN = new List<string>();
List<string> FN = new List<string>();
List<string> GN = new List<string>();
List<string> HN = new List<string>();
using (OracleConnection connection = new OracleConnection(sConnectionString))
{
connection.Open();
using (OracleCommand command = new OracleCommand("SELECT NVL(AName,0),NVL(BName,0),NVL(CName,0),NVL(DName,0),NVL(EName,0),NVL(FName,0),NVL(GName,0),NVL(HName,0) FROM T_CSP where REP_DATE BETWEEN :d1 AND :d2 order by REP_DATE", connection))
{
command.Parameters.Add(new OracleParameter(":d1", dt1));
command.Parameters.Add(new OracleParameter(":d2", dt2));
command.BindByName = true;
using (OracleDataReader reader = command.ExecuteReader())
{
while (reader.Read())
{
AN.Add(reader[0].ToString());
BN.Add(reader[1].ToString());
CN.Add(reader[2].ToString());
DN.Add(reader[3].ToString());
EN.Add(reader[4].ToString());
FN.Add(reader[5].ToString());
GN.Add(reader[6].ToString());
HN.Add(reader[7].ToString());
}
}
connection.Close();
}
}
Points at a Glance
- sConnectionString is your connection string which can be set dynamically or statically or in your application's configuration file.
- Any valid SQL Query can be used.
- d1 and d2 are the parameters, more precisely date parameters. If dynamic fiscal date is to be set check out the link below.
- AN is a list string that will contain all the fields of column AName in table T_CSP between date d1 and d2 order by rep_date. Similarly BN is a list string that will contain all the fields of column BName in table T_CSP between date d1 and d2 order by rep_date.
- Rest all the list strings will have fields of their respective columns.
This is how we can read multiple columns in different list strings.
Thursday, 9 February 2017
Save and retrieve credentials in C# Windows form application
While developing a windows form application which accepts some details from the user, you might want to provide user a feature to remember those details and if user chooses to remember his details then the next time he will run the application, credentials will be auto-populated for quick log in.
Now firstly lets see how to save details in a file....
In any application the main source of details from user is a text box, hence in here also we ll use text box as the main source of information from the user. Also we might want to provide user an option if he wants to save his details or not. So for this purpose we'll use a check box control. Also for the sake of convenience we'll save each credential in separate line so that retrieving the becomes easy.
Also we'll use ".dat" file extension to save the file. We could use ".txt" also but using .dat is good for security purposes. Also user would not try to modify it but .txt is an extension common to all so a user may try to modify it.
The file should be saved at current directory that is the directory where the user will install our application, hence we won't be specifying any path while saving or retrieving the file.
Also for efficiency of your application we should save the user credentials only after the current thread is executed properly as there might arise a case when user may have entered wrong detail. We might not want to save erroneous details. So Before saving his details we should verify and validate the user data first, if its not correct then an error should be displayed and user should be offered a chance to enter his credentials again till the time he enters correct credentials.
Also we should clear the contents of the file every time a user checks the checkbox, just to mantain correctness and consistency of the file.
Source Code for saving the credentials in the file
if (chkBx_Remember.Checked) //check if check box is checked
{
System.IO.File.WriteAllText(@"winform.dat", string.Empty); // empty contents of file
save.Add(txt_UserName.Text);
save.Add(txt_Password.Text);
save.Add(txt_Host.Text);
save.Add(txt_PortNo.Text);
save.Add(txt_ServiceName.Text);
{
foreach (String s in save)
tw.WriteLine(s); //Each credential will be saved in separate line
}
}
Now lets see how to retrieve data from file and populate the respective text box
Since we have stored the details in the file we should also retrieve them, off course that is the reason we saved the details in the file.
Also we should include the retrieving logic while loading the thread on which we want to populate the details off course. Generally for an application a login thread is the foremost so its better to include this logic in Form1_Load method(default).
We should first check if the file exists, because file will not be present if user has not saved any details or he might be logging in for the first time what so ever the reason may be.
Source Code for retrieving details from the file
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
{
String line;
System.IO.StreamReader file = new System.IO.StreamReader(@"winform.dat");
while ((line = file.ReadLine()) != null)
{
f_details.Add(line);
}
file.Close();
txt_Password.Text = f_details[1];
txt_Password.UseSystemPasswordChar = true;
txt_Host.Text = f_details[2];
txt_PortNo.Text = f_details[3];
txt_ServiceName.Text = f_details[4];
}
}
Also we'll use ".dat" file extension to save the file. We could use ".txt" also but using .dat is good for security purposes. Also user would not try to modify it but .txt is an extension common to all so a user may try to modify it.
The file should be saved at current directory that is the directory where the user will install our application, hence we won't be specifying any path while saving or retrieving the file.
Also for efficiency of your application we should save the user credentials only after the current thread is executed properly as there might arise a case when user may have entered wrong detail. We might not want to save erroneous details. So Before saving his details we should verify and validate the user data first, if its not correct then an error should be displayed and user should be offered a chance to enter his credentials again till the time he enters correct credentials.
Also we should clear the contents of the file every time a user checks the checkbox, just to mantain correctness and consistency of the file.
Source Code for saving the credentials in the file
if (chkBx_Remember.Checked) //check if check box is checked
{
// check if file exist in current directory
if (File.Exists("winform.dat")) System.IO.File.WriteAllText(@"winform.dat", string.Empty); // empty contents of file
//Array list to save each credential at different index
List<String> save = new List<String>();save.Add(txt_UserName.Text);
save.Add(txt_Password.Text);
save.Add(txt_Host.Text);
save.Add(txt_PortNo.Text);
save.Add(txt_ServiceName.Text);
//write data in the file line by line if it exist or create a new file if file doesn't exist
using (TextWriter tw = new StreamWriter("winform.dat")){
foreach (String s in save)
tw.WriteLine(s); //Each credential will be saved in separate line
}
}
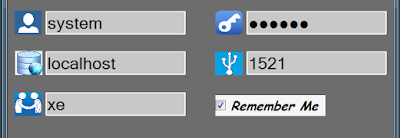 |
| Saving details in file |
Now lets see how to retrieve data from file and populate the respective text box
Since we have stored the details in the file we should also retrieve them, off course that is the reason we saved the details in the file.
Also we should include the retrieving logic while loading the thread on which we want to populate the details off course. Generally for an application a login thread is the foremost so its better to include this logic in Form1_Load method(default).
We should first check if the file exists, because file will not be present if user has not saved any details or he might be logging in for the first time what so ever the reason may be.
Source Code for retrieving details from the file
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Check if the file exists in the current directory
if (File.Exists("winform.dat")){
// Array list to retrieve each credential at different index
List<string> f_details = new List<string>() { };String line;
System.IO.StreamReader file = new System.IO.StreamReader(@"winform.dat");
while ((line = file.ReadLine()) != null)
{
f_details.Add(line);
}
file.Close();
// Populating the credentials in their respective text box
txt_UserName.Text = f_details[0];txt_Password.Text = f_details[1];
txt_Password.UseSystemPasswordChar = true;
txt_Host.Text = f_details[2];
txt_PortNo.Text = f_details[3];
txt_ServiceName.Text = f_details[4];
}
}
Wednesday, 8 February 2017
On 23:06 by Vardan Kumar in C# No comments
ToolTip for controls in c# Windows Form Application
While developing a windows form application, most of us come around with designing its GUI(Graphical User Interface). Since the inclusive toolbox in visual studio inhibits certain features in a windows form application, hence we have to build our own logic for the same. So what's there in designing which makes us do this work as we can just develop an application to just do our intended work. Wish it was so simple but it doesn't work like this when it comes to the real world. In the real world Appearance leads to Pursuance.
So what exactly a ToolTip does?
It is a clue more precisely an info used to brief what a tool does. This tool is used in association with the mouse cursor usually a pointer or sometimes an I-cursor for certain controls like text box without clicking it. After successfully implementing a tool tip in your GUI(Graphical user Interface) a small rectangular pop-up window must appear next to your control which is being hovered to displaying what this control does.
Now let us see its implementation in c#....
1. Create and initialize an instance of a class called as ToolTip. It is a class under System.Windows.Forms.ToolTip.
ToolTip tt = new ToolTip();
2. Associate ToolTip Text with specified control.
//Fetches path of current directory and assign to label
lbl_Path.Text = System.IO.Directory.GetCurrentDirectory();
//SetToolTip(Control name,"Hibt you want to give");
tt.SetToolTip(lbl_Path, lbl_Path.Text);
 |
| ToolTip on label control(Text greater than Window Form size) |
3. You can use same instance(here tt) to provide hit to various other control.
tt.SetToolTip(txt_UserName, txt_UserName.Text);
tt.SetToolTip(txt_Host, txt_Host.Text);
 |
| ToolTip on TextBox(Text greater than TextBox size) |
If you want to change your ToolTip for a text box as the text in the same changes then register TextChnaged event for the same.
private void txt_UserName_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
tt.SetToolTip(txt_UserName, txt_UserName.Text);
}
private void txt_Host_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
tt.SetToolTip(txt_Host, txt_Host.Text);
}
Generally you might want to associate ToolTip with control under Form1_Load.
One of the major application of ToolTip apart from displaying what a control does is displaying the text on control for which our text associated with that control is greater than are window size.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Search
Popular Posts
-
Troubleshooting Cisco VPN client Before starting troubleshooting, Let us see what VPN is and what it requires to perform its intended f...
-
File Versioning C# File versioning, saving file with unique file name in c# File versioning allows a user to have several versions of ...
-
Evolution-Mobile Phones With the development of portable technology,wireless communication has so evolved that (According to the announce...
-
Text Box Hint in c# Windows Form Application Text Box Hint in c# Windows Form Application While developing a windows form applicat...
-
Unable to set the Freeze Panes property of Window Class C# It is generally easy to resolve the compile time errors because the reason fo...